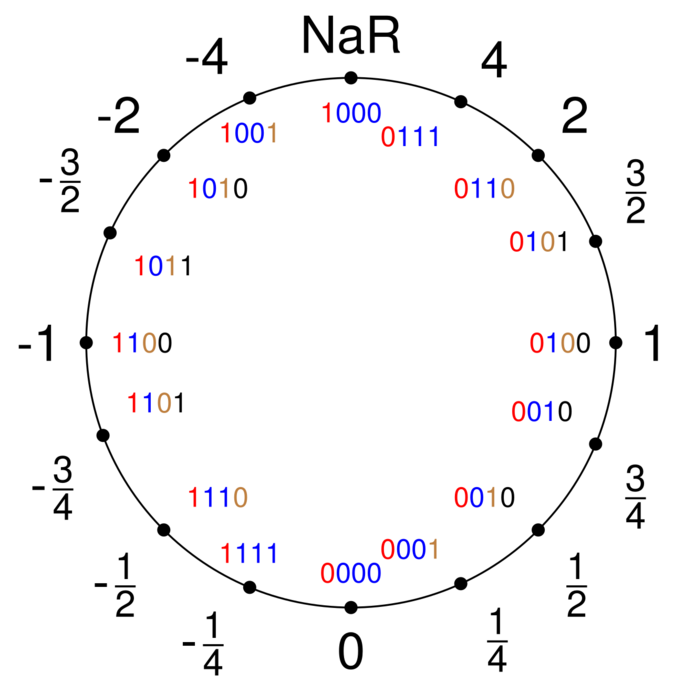
The Posit number format is an alternative floating point format that was developed to overcome the limitations of the widely used IEEE 754 standard, particularly in terms of precision and handling extreme values. It uses a variable number of bits for exponent and mantissa, based on the so-called regime, which represents the order of magnitude of the number. This allows Posit to offer higher precision for smaller numbers and at the same time cover a larger dynamic range than conventional floating point numbers with the same bit width. Rounding errors are to be minimized using unums (universal number).
The first GPUs based on Posits are now available (see here).
In the context of this thesis, posits are to be implemented in a modern hardware description language (Chisel or Clash) and evaluated on FPGAs.
References
- Gustafson, John L. Every Bit Counts: Posit Computing. 978-1-032-73805-5. Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2024. https://www.routledge.com/Every-Bit-Counts-Posit-Computing/Gustafson/p/book/9781032738055
- Posit Working Group. "Standard for Posit Arithmetic (2022)," March 2, 2022. https://posithub.org/docs/posit_standard-2.pdf
- Schärtl, A. Unums and Posits: A Replacement for IEEE 754 Floating Point? 2021. Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg
- Unum & Posit - Next Generation Aithmetic. PositHub https://posithub.org/
- Gustafson, John L. The End of Error: Unum Computing. 978-1-4822-3986-7. Apple Academic Press Inc., 2015
Contact
Oliver Keszöcze
Professor of Computer Engineering
E-Mail: oliver.keszoecze@tu-clausthal.de
Telephone: +49 5323 72-7153
